Ajit Govind Sable s family has owned their farm in India s western Maharashtra state for 10 generations, which even for a region that has been farming for more than 10,000 years is long enough to witness plenty of changes.
Two generations back, they started cultivating sugar cane here in Shivthar, a village in Maharashtra s highlands near the Krishna River. India s most industrialized state soon became its largest sugar producer.
Today, it s not sugar the 35-year-old Sable is talking about as he sips sweet tea in the front yard of the low, two-storey farmhouse where half the ground floor houses his turmeric crop. He s discussing peppers, which he is now growing under polythene plastic coverings.
Read Also
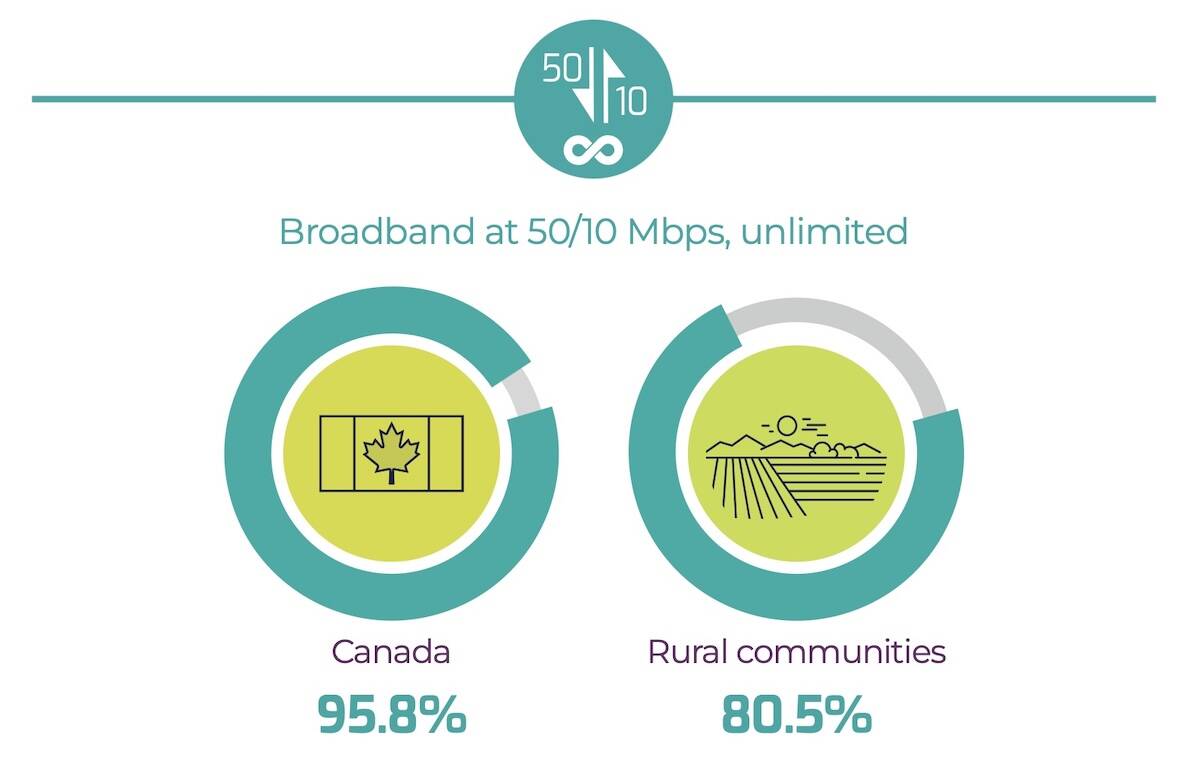
Rural Alberta gets further boost to internet connectivity
The province and feds join forces to help remote/rural Albertans get connected to reliable high-speed internet through its Broadband Strategy.
Like an increasing number of farmers in India, Sable is exploiting a shift in taste towards fruits and vegetables among Indians. My colleagues grow flowers under poly, Sable says. But the investment for that is too much for me, so I m trying out peppers. You can t eat flowers if you can t find buyers for them, he notes.
While many Indian farmers are eager to adjust to changing diets in one of the world s fastest-growing markets, the government continues to subsidize the cultivation of wheat, sugar and rice crops to ensure basic food needs for the country s half a billion poor.
The result is overflowing stocks of these carbohydrate-heavy staples and a huge subsidy bill that is adding to a ballooning budget deficit.
India, many agricultural experts say, is spending billions to prop up a traditional farm sector at the expense of investment in new crops and agricultural innovation.
But in a country where one out of five Indians goes hungry, the government has had to focus on foods that fuel or fill carbohydrate-heavy wheat, rice and sugar. About 36 per cent of women and 34 per cent of men in India are underweight. The costs of that undernourishment is high in terms of health care, lost productivity and poor quality of life.
At the same time, a growing urban middle class is consuming more higher-value, high-protein foods, which is stoking food price inflation as well as changing business and farm models in rural India.
The food chain in India is undergoing deep change.
There is a view that this is a structural shift and pulses, milk, meat, eggs, fish, protein items these are sectors where you need to concentrate, Abhijit Sen, who sits on the government s planning committee, said in a speech on June 5.
Rising middle class
Those shifts have been underway for years but are accelerating with rapid urbanization and the expansion of India s middle class. India is getting wealthier as well as healthier.
Its eight per cent annual growth, second only to China among major countries, is boosting incomes rapidly in the trillion-dollar economy. Per capita income surged to $1,265 in 2010 from $857 in 2006 a nearly 50 per cent increase according to the World Bank and IMF.
Middle-class households are expected to grow 67 per cent in the next five years, bringing over 53 million households into an annual income bracket between 340,000 and 1.7 million rupees ($7,600-$38,000).
Bijay Kumar, managing director of the National Horticulture Board, says having more money than your parents is pushing up demand for high-protein foods.
Rising income levels are allowing people to spend on high-value stuff, he says. People are more aware of health. They are increasing their intake of fruits in their regular diet.
In 2009-10, Indians boosted spending on fruit and vegetables by nearly nine per cent over the year earlier. They shelled out almost 31 per cent more on meat, eggs and fish. Spending on cereals, on the other hand, was flat.
A dietary transformation is underway in the country and demand for high-value, vitamin-and protein-rich food such as fruit, vegetables, milk, eggs, poultry, meat and fish is increasing, the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) said in a study this year.
Food security
Years of eating an oil-rich, sugary diet high in carbohydrates have left many Indians with a paunch and a health problem. India has the world s largest diabetes population at just below 51 million people, while heart disease is the single-largest cause of death.
Yet hunger is endemic among the country s 500 million poor. The government of Prime Minister Manmohan Singh is drafting a Food Security Act that promises to expand subsidized wheat and rice well beyond the current 30 per cent of the population in a country that is home to 40 per cent of the world s malnourished children.
That could mean India spending about $25 billion a year on providing cheap food or about nine per cent of total spending this year more than four times the expenditure on health care.
While the farm sector is slowly diversifying, it is a declining contributor to growth, despite providing a living to more than half the country s workforce. About 600 million Indians are dependent on farming half the population of 1.2 billion even though agriculture makes up only 14.6 per cent of the economy and has been declining from 30 per cent a decade ago.
The average size of farms in India is a mere 1.33 hectares about the size of two soccer pitches and that figure has been steadily declining.
Farmers are finding it ever more difficult to make ends meet. The introduction of high-yielding seed varieties and increased use of fertilizers and irrigation spawned the Green Revolution in the 1960s that allowed India to become self-sufficient in grains. But experts say agriculture innovation and efficiency has stalled in recent years and farmers are getting squeezed by rising costs and inefficient agronomy.
Since the mid-1990s, an estimated 150,000 small farmers have committed suicide, according to the Center for Human Rights and Global Justice at New York University, most of them over debts.
Increasingly, voices in government and among experts are calling for a different approach, one that curbs subsidy spending, tackles inflation and boosts agricultural production of higher-value foods.














